Difference between revisions of "ProvaTeorica 2013.02.15"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Stefano 92 (talk | contribs) |
|||
| (4 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 118: | Line 118: | ||
z t z t z | z t z t z | ||
| − | 0 0 0 0 | + | 0 0 0 0 0 |
| − | 0 1 1 0 | + | 0 1 1 0 1 |
| − | 1 0 1 1 | + | 1 0 1 1 0 |
| − | 1 1 0 1 | + | 1 1 0 1 1 |
| − | void Swap( | + | void Swap(bool z, bool t){ |
| − | + | bool tmp; | |
z=t; | z=t; | ||
t=tmp; | t=tmp; | ||
| Line 131: | Line 131: | ||
<h2> Esercizio g.1 </h2> | <h2> Esercizio g.1 </h2> | ||
[[File:RoundRobin2cpu.png]] | [[File:RoundRobin2cpu.png]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | {| border="1" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |TEMPO | ||
| + | |1 | ||
| + | |2 | ||
| + | |3 | ||
| + | |4 | ||
| + | |5 | ||
| + | |6 | ||
| + | |7 | ||
| + | |8 | ||
| + | |9 | ||
| + | |10 | ||
| + | |11 | ||
| + | |12 | ||
| + | |13 | ||
| + | |14 | ||
| + | |15 | ||
| + | |16 | ||
| + | |17 | ||
| + | |18 | ||
| + | |19 | ||
| + | |20 | ||
| + | |21 | ||
| + | |22 | ||
| + | |23 | ||
| + | |24 | ||
| + | |25 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |CPU 1 | ||
| + | |P1 | ||
| + | |P1 | ||
| + | |P1 | ||
| + | |P1 | ||
| + | |P4 | ||
| + | |P4 | ||
| + | |P4 | ||
| + | |P4 | ||
| + | |P4 | ||
| + | |P4 | ||
| + | |P4 | ||
| + | |P4 | ||
| + | |P4 | ||
| + | |P4 | ||
| + | |P4 | ||
| + | |P4 | ||
| + | |P3 | ||
| + | |P3 | ||
| + | |P3 | ||
| + | |P4 | ||
| + | |P1 | ||
| + | |P1 | ||
| + | |P1 | ||
| + | |P1 | ||
| + | |P1 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |CPU 2 | ||
| + | |P2 | ||
| + | |P2 | ||
| + | |P3 | ||
| + | |P3 | ||
| + | |P3 | ||
| + | |P1 | ||
| + | |P2 | ||
| + | |P2 | ||
| + | |<br> | ||
| + | |P3 | ||
| + | |P3 | ||
| + | |P3 | ||
| + | |<br> | ||
| + | |P1 | ||
| + | |P1 | ||
| + | |P2 | ||
| + | |P2 | ||
| + | |P2 | ||
| + | |P2 | ||
| + | |P2 | ||
| + | |<br> | ||
| + | |<br> | ||
| + | |<br> | ||
| + | |<br> | ||
| + | |<br> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |I/O | ||
| + | |<br> | ||
| + | |<br> | ||
| + | |P2 | ||
| + | |P2 | ||
| + | |P2 | ||
| + | |P2 | ||
| + | |P3 | ||
| + | |P3 | ||
| + | |P3 | ||
| + | |P1 | ||
| + | |P1 | ||
| + | |P1 | ||
| + | |P1 | ||
| + | |P2 | ||
| + | |P3 | ||
| + | |P1 | ||
| + | |P1 | ||
| + | |P1 | ||
| + | |P1 | ||
| + | |P1 | ||
| + | |P4 | ||
| + | |<br> | ||
| + | |<br> | ||
| + | |<br> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | Domanda: una soluzione del genere sarebbe corretta? | ||
| + | -Stefano 92 | ||
Latest revision as of 16:58, 15 May 2014
Testo del compito
Esercizio c.1
/*
Esercizio c.1: (a) Scrivere un monitor dualwriter che realizzi un doppio buffer limitato (ogni buffer ha ampiezza
BUFSIZE) che consenta a uno scrittore di scrivere contemporaneamente due elementi che andranno rispettivamente
nel primo e nel secondo buffer. Le letture :
procedure entry void write(type1 e1, type2 e2);
procedure entry type1 read1();
procedure entry type2 read2();
La funzione write deve attendere che ci sia spazio in entrambi i buffer.
La funzione read attende che vi sia almeno un elemento nel buffer indicato
*/
monitor dualwriter
{
type1* buffer1;
type2* buffer2;
condition oktowrite,oktoread1, oktoread2
procedure entry void write (type1 e1, type2 e2)
{
if (sizeof(type1)>=BUFSIZE || sizeof(type2)>=BUFSIZE)
oktowrite.wait();
buffer1.push(e1);
buffer2.push(e2);
oktoread1.signal();
oktoread2.signal();
}
procedure entry type1 read1()
{
if (sizeof(buffer1)==0)
oktoread1.wait();
buffer1.pop();
if (sizeof(buffer2)<BUFSIZE)
oktowrite.signal();
}
procedure entry type2 read2()
{
if (sizeof(buffer2)==0)
oktoread2.wait();
buffer2.pop();
if (sizeof(buffer1)<BUFSIZE)
oktowrite.signal();
}
}
-stefano92
monitor dualwriter{
queue buffer1;
queue buffer2;
condition oktowrite;
condition oktoread1;
condition oktoread2;
procedure entry void write(type1 e1, type2 e2){
if((buffer1.len() == BUFSIZE) || (buffer2.len() == BUFSIZE)) /*se uno dei due buffer è pieno non puoi inserire*/
oktowrite.wait();
buffer1.enqueue(e1);
buffer2.enqueue(e2);
oktoread1.signal();
oktoread2.signal();
}
procedure entry type1 read1(){
if(buffer1.len() == 0) /*buffer vuoto*/
oktoread1.wait();
buffer1.dequeue;
oktowrite.signal();
}
procedure entry type2 read2(){
if(buffer2.len() == 0) /*buffer vuoto*/
oktoread2.wait();
buffer2.dequeue;
oktowrite.signal();
}
}
Giulia
Esercizio c.2
// foo(x,y) <x=2+y , y=2+x>
int g = 0;
csenter:
do
int l;
foo(l, g);
while(l!=2)
csexit:
g = 0;
// bar (z,t) <z= z xor t, t= t xor z, z = z xor t>
z t z t z
0 0 0 0 0
0 1 1 0 1
1 0 1 1 0
1 1 0 1 1
void Swap(bool z, bool t){
bool tmp;
z=t;
t=tmp;
}
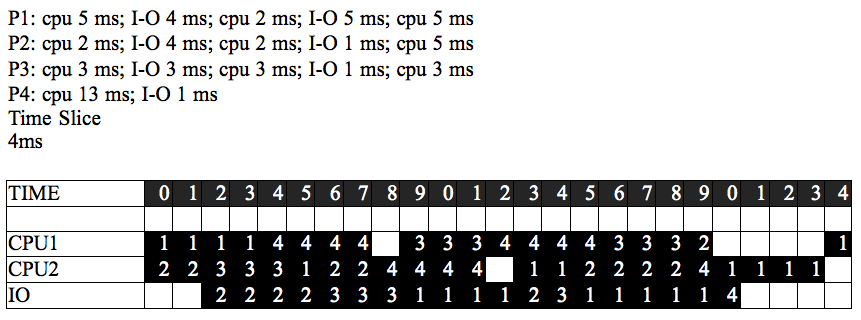
Esercizio g.1
| TEMPO | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 |
| CPU 1 | P1 | P1 | P1 | P1 | P4 | P4 | P4 | P4 | P4 | P4 | P4 | P4 | P4 | P4 | P4 | P4 | P3 | P3 | P3 | P4 | P1 | P1 | P1 | P1 | P1 |
| CPU 2 | P2 | P2 | P3 | P3 | P3 | P1 | P2 | P2 | P3 | P3 | P3 | P1 | P1 | P2 | P2 | P2 | P2 | P2 | |||||||
| I/O | P2 | P2 | P2 | P2 | P3 | P3 | P3 | P1 | P1 | P1 | P1 | P2 | P3 | P1 | P1 | P1 | P1 | P1 | P4 |
Domanda: una soluzione del genere sarebbe corretta? -Stefano 92